- March 3, 2025
- Posted by: feinuojixie
- Category: Injection Molding News

Injection molded part is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unmatched precision, efficiency, and design versatility. From automotive components to consumer electronics, this manufacturing process enables the mass production of high-quality parts with consistent performance.
The significance of injection molded part lies in its ability to produce complex geometries at a lower cost compared to other manufacturing methods. The combination of advanced materials, automated systems, and cutting-edge technology has revolutionized the way industries approach product development.
In this guide, we will explore everything about injection molded part—from the fundamental process to innovative advancements shaping the industry. Whether you are an engineer, product designer, or manufacturer, this comprehensive resource will provide valuable insights to enhance your knowledge and optimize your production strategy.
Understanding Injection Molded Part: Basics and Process
Injection molded part is manufactured using a highly efficient and repeatable process known as injection molding. This technique involves injecting molten material, typically a thermoplastic or thermosetting polymer, into a precisely designed mold cavity under high pressure. Once cooled and solidified, the part is ejected, ready for use.
The process consists of several key stages:
Clamping – The mold is securely closed to withstand high-pressure injection.
Injection – Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity.
Cooling – The material solidifies within the mold, taking its final shape.
Ejection – The finished part is pushed out of the mold for further processing.
This automated method allows for high production efficiency, making injection molded part a preferred choice for industries requiring mass production with minimal variation.


Advantages of Injection Molded Part in Manufacturing
The popularity of injection molded part stems from its numerous advantages:
High Precision and Consistency – Every part produced maintains identical specifications, ensuring uniformity.
Cost-Effectiveness for Large-Scale Production – Once the mold is developed, per-unit costs decrease significantly.
Design Flexibility – Complex shapes, intricate details, and undercuts can be easily achieved.
Material Efficiency and Sustainability – Excess material can often be recycled, reducing waste.
These benefits make injection molded part essential in industries such as automotive, medical devices, consumer goods, and aerospace.
Key Components of an Injection Molded Part
To achieve superior quality, several design considerations must be made:
Mold Design – A well-crafted mold ensures dimensional accuracy and efficient production.
Wall Thickness – Uniform wall thickness prevents defects like warping and sink marks.
Draft Angles – Slight angles facilitate easy part ejection, preventing damage.
Gate Placement – Proper gate positioning controls material flow, ensuring complete cavity filling.
Cooling System – A well-designed cooling mechanism minimizes cycle time and enhances part quality.
By optimizing these factors, manufacturers can achieve a high-performance injection molded part with minimal defects.
Innovations in Injection Molded Part Technology
With rapid technological advancements, the injection molding industry continues to evolve:
Advanced Materials – High-performance plastics, biodegradable polymers, and reinforced composites enhance durability and sustainability.
3D Printing for Mold Prototyping – Additive manufacturing accelerates mold development, reducing lead time and cost.
AI-Driven Optimization – Smart sensors and artificial intelligence improve process efficiency and defect detection.
Eco-Friendly Manufacturing – The shift toward sustainable materials and energy-efficient machinery is reducing the environmental impact of injection molded part production.
These innovations pave the way for a more efficient and environmentally responsible manufacturing landscape.
Common Defects in Injection Molded Part and How to Prevent Them
Despite its precision, injection molding can encounter defects. Understanding their causes helps prevent costly production issues:
Warping – Uneven cooling causes distortion; optimizing mold design and cooling rates minimizes this issue.
Sink Marks – Excess material shrinkage creates surface indentations; maintaining uniform wall thickness reduces the risk.
Flash – Excess material leaks at the mold parting line; ensuring proper clamping pressure prevents this defect.
Short Shots – Incomplete filling of the mold cavity leads to missing sections; increasing injection pressure solves this problem.
Air Bubbles – Trapped air causes voids within the part; using proper venting and adjusting injection speed prevents bubbles.
Implementing strict quality control measures ensures consistent and defect-free production.
Choosing the Right Material for an Injection Molded Part
Material selection significantly influences the performance of an injection molded part. The most commonly used materials include:
Polypropylene (PP) – Lightweight, durable, and resistant to chemicals.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) – Strong, impact-resistant, and easy to mold.
Polycarbonate (PC) – Transparent, heat-resistant, and highly durable.
Nylon (PA) – High strength, wear resistance, and excellent mechanical properties.
Polyethylene (PE) – Flexible, moisture-resistant, and cost-effective.
Choosing the appropriate material depends on factors like mechanical strength, thermal stability, and environmental impact.
Cost Factors and Efficiency in Injection Molded Part Production
To optimize costs and maximize efficiency, manufacturers must consider:
Mold Development Costs – High upfront investment, but cost-effective for mass production.
Cycle Time Optimization – Reducing cooling and injection times enhances productivity.
Automation and Robotics – Implementing automated systems lowers labor costs and increases consistency.
Material Selection – Choosing cost-effective yet high-quality materials ensures long-term savings.
By refining these elements, companies can achieve an optimal balance between cost and quality.
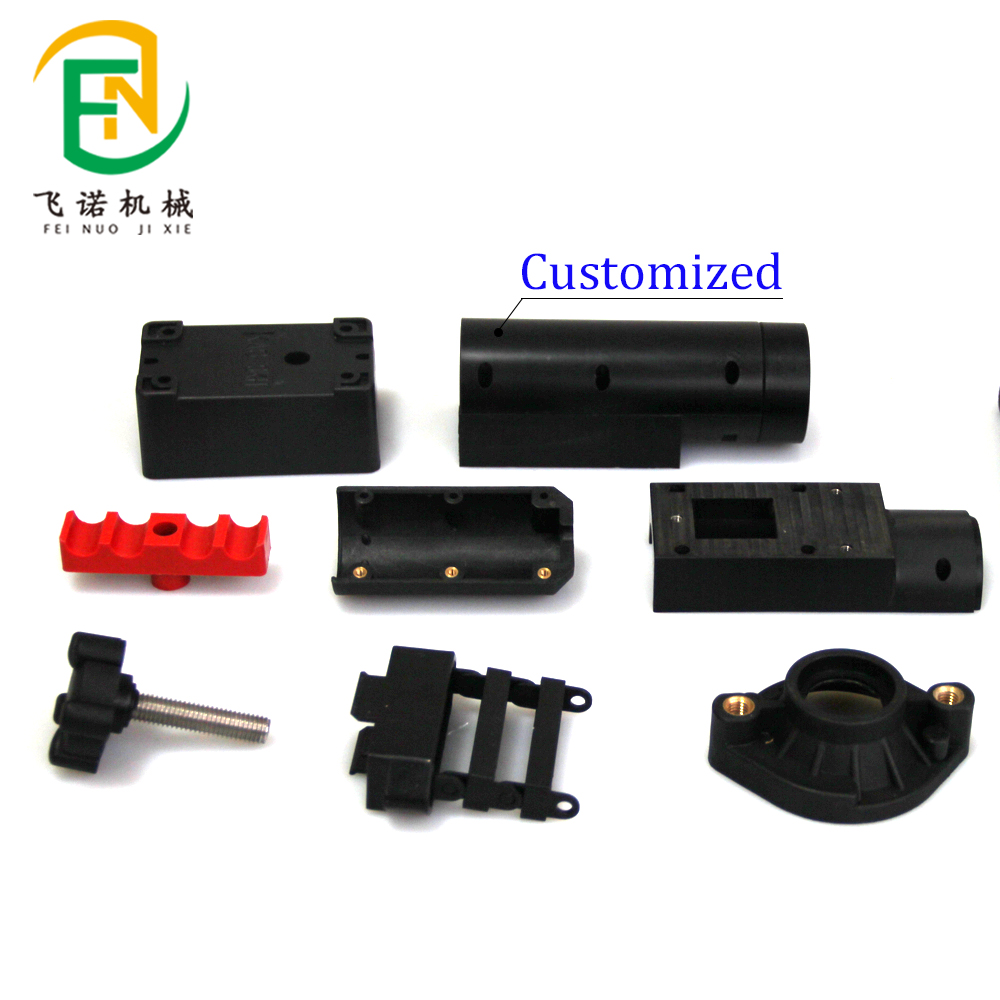


Future Trends in Injection Molded Part Manufacturing
The future of injection molded part production is driven by technological advancements:
Sustainable and Biodegradable Materials – Growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives is reshaping material choices.
Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 – Integration of IoT, AI, and machine learning enhances process control.
Nanotechnology in Polymers – Improved material properties lead to stronger and lighter parts.
Hybrid Manufacturing Techniques – Combining injection molding with 3D printing expands design possibilities.
These trends will continue to redefine efficiency, sustainability, and innovation in the industry.
Conclusion
Injection molded part remains a fundamental component of modern manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. With continuous advancements in materials, automation, and process optimization, the industry is set to become more sustainable and technologically sophisticated.
As manufacturers and designers explore new innovations, embracing smart manufacturing techniques and eco-friendly practices will be crucial in shaping the future of injection molded part production. By staying informed and adapting to industry trends, businesses can maintain a competitive edge and drive long-term success.
